Who should read this article: Administrators
How to use custom and system variables in Flow Builder to enable interaction routing automation and contact data retrieval.
Introduction
Using variables in your interaction flows enables you to automate interaction handling and permit self-service for your contacts.
Flow Builder supports both system and custom variables. System variables are predefined; they allow you to capture and reuse information about the interaction. Custom variables, which you define, enable you to reuse data from a request response elsewhere in your interaction flow and develop flexible custom routing logic. Variables facilitate passing data from node to node and making routing decisions based on their values.
System variables
The following five system (global) variables are available for voice interactions:
| Variable | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
{{start_time}} |
The time the interaction started. | 2023-08-21T04:02:18Z |
{{ani}} |
The calling number (ANI). | 443336006114 |
{{dnis}} |
The number dialed (DNIS). | 380631234567 |
{{phone_type}} |
The type of phone for the ANI. | fixed_line |
uuid |
a string containing the UUID of the interaction | 07771c38-c159-4965-a878-be0162118b2b |
The following system (global) variables are available for digital interactions:
| Variable | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
{{from}} |
A string containing the user's ID for the digital channel. | 55555555555 |
{{to}} |
A string containing the ID of the channel to which the user sent an interaction. | 55555555555 |
{{start_time}} |
The time the interaction started. | 2023-08-21T04:02:18Z |
{{uuid}} |
A string containing the UUID of the interaction. | 07771c38-c159-4965-a878-be0162118b2b |
Custom variables
Some nodes support the use of custom variables that you can use to store information to pass to other nodes and use for routing decisions or to retrieve data from a data service and send data to contacts.
Variable names
You can use a string of up to 60 characters to name your variables. The following characters cannot be used in character name: { and }.
Types
The following data types are supported for custom variables:
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
String |
Maximum string length is 4096 characters. Used for storing names, URLs, and other text-based information. | "Isabela García" or "https://myservice.com/bal?q={{var}}" |
Number |
Any numerical value up to 255 digits. Both integers and floating point numbers are supported. | "199.95" or "16" |
Datetime |
A single date and time in the following format: YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS |
"2024-04-17 13:45:30" |
Some data types are not supported for variables in certain nodes. For example, datetime is not supported for the Route node.
Nodes
The following nodes support the use of variables. Refer to the individual node articles for information about how to configure and use variables with the node.
| Node | Description | System | Custom | Restrictions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collect digits | Enables you to gather and store dial pad key-presses from callers. This functionality enhances data-driven routing and enables the development of a self-service IVR. | ✔ |
✔ |
None |
| Conditions | Enables the analysis and comparison of variables of all types, including system and custom variables, such as strings, numbers, or date and time values against a static value or another variable. | ✔ |
✔ |
None |
| HTTP Request | Enables you to define and use custom variables to store a data key from an HTTP request response using the JSONPath expression. | ✔ |
✔ |
None |
| Message | Enables you to insert dynamic content into the body of a message or save a contact response. | ✔ |
✔ |
None |
| Route | Enables you to specify a variable to contain an agent name or extension, a queue extension, or an external phone number (voice only). | ✖ |
✔ |
None |
| Send Message | Enables you to insert dynamic content into the body of an SMS message | ✔ |
✔ |
Not supported for WhatsApp messages. |
Variable menu
When a menu or field supports the use of variables, the { } menu button is added to the field. Click { } to display the Variables menu.
The Variables menu enables you to select from any of the system variables and any custom variables you have defined.
Some nodes have a dedicated Variable menu. Click the menu to select an existing custom variable to be used by the node.
Adding variables manually
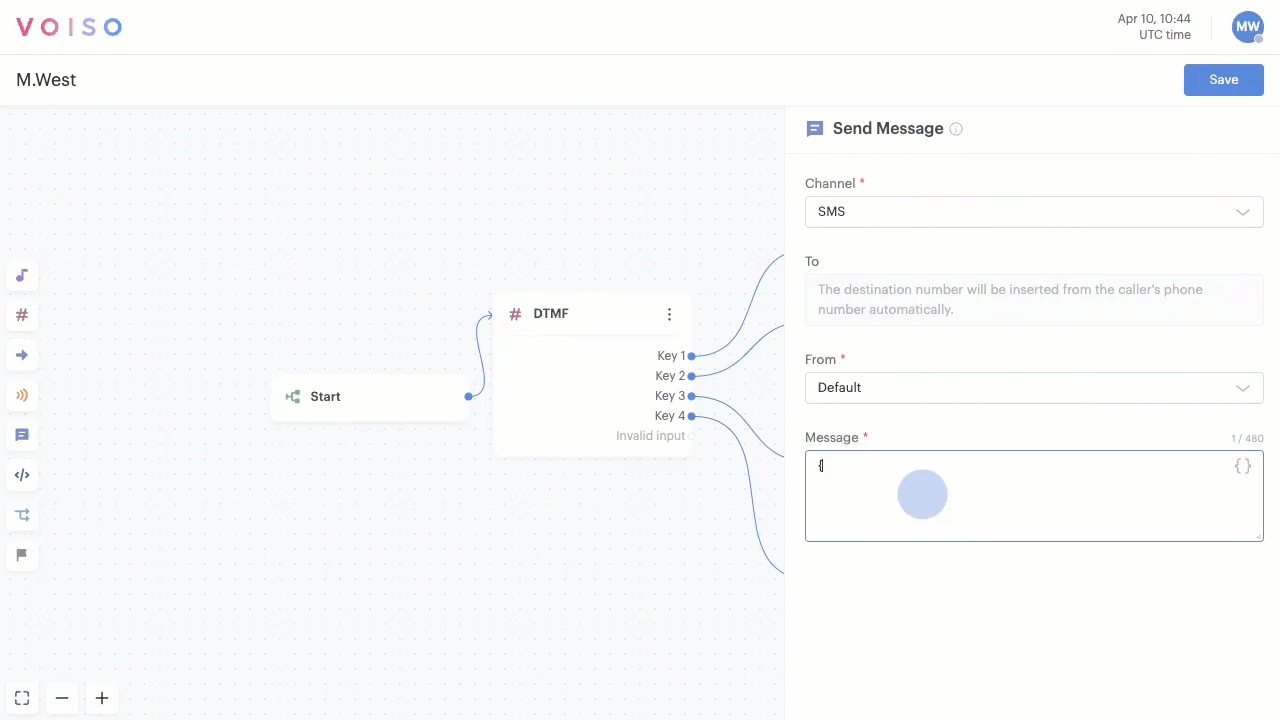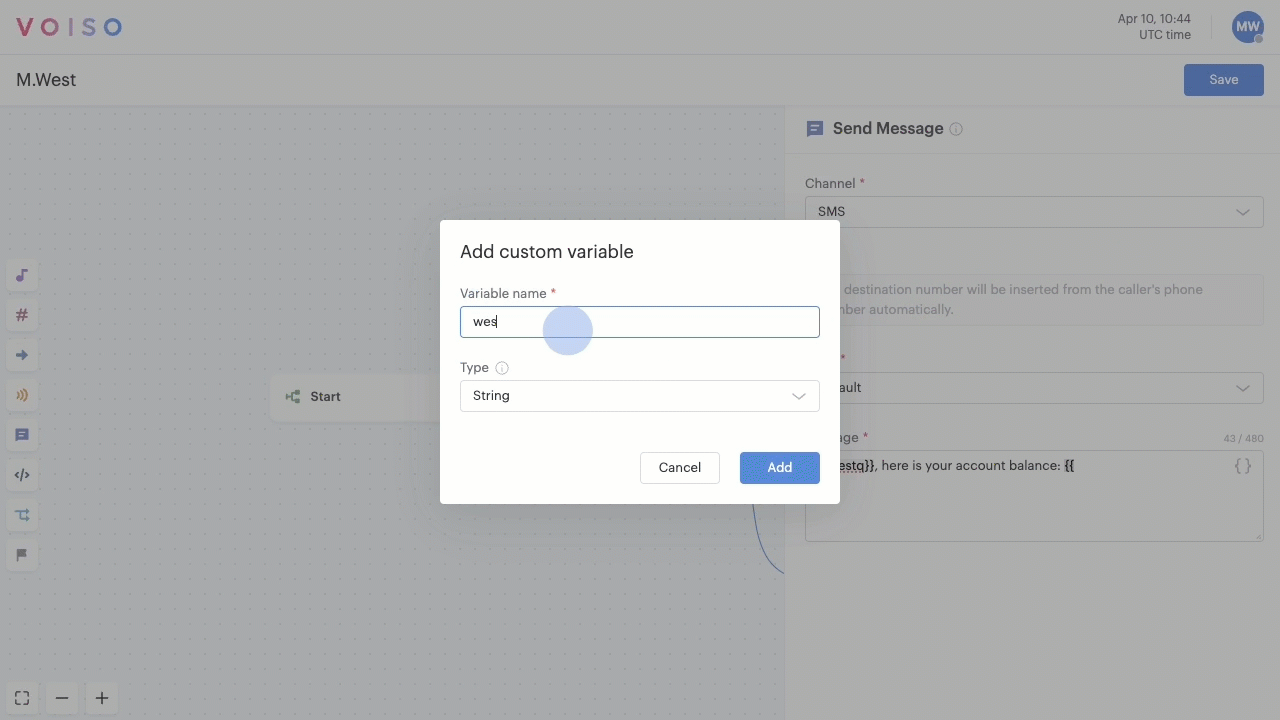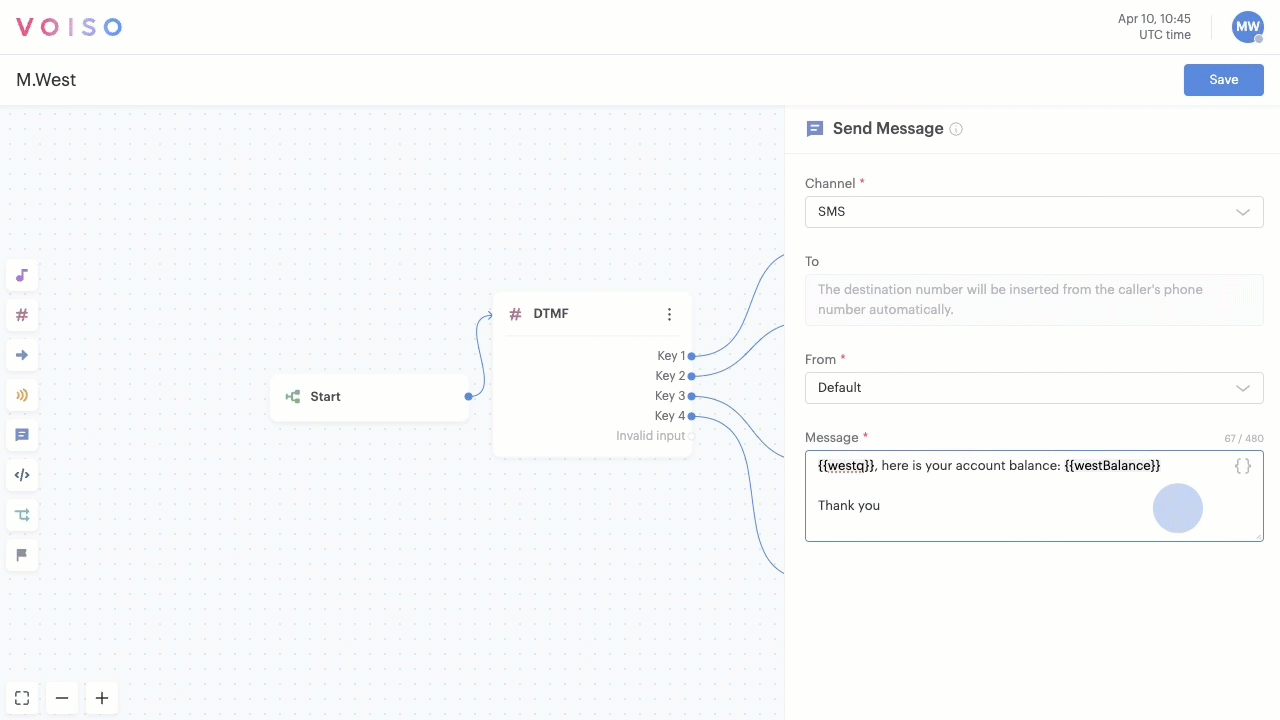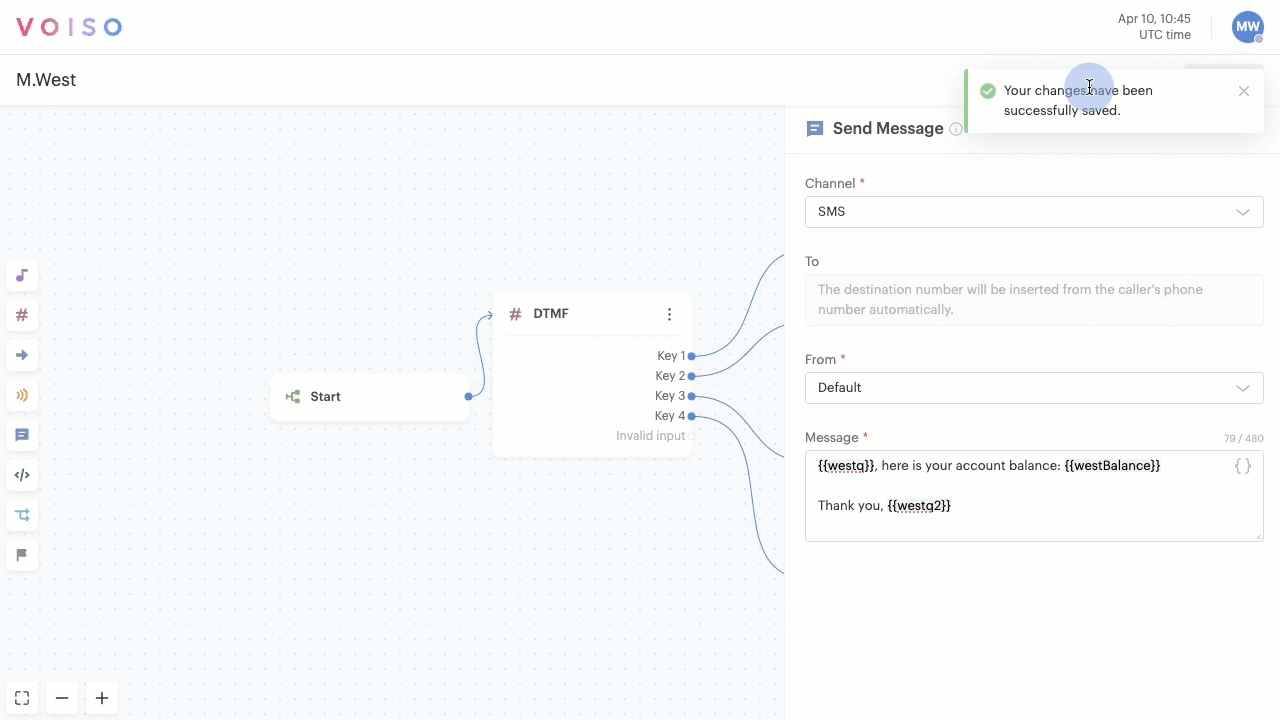
In fields and text boxes that permit variables, you can type "{{" to start entering variables manually. If you type a variable name that has not already been created, the Add custom variable panel displays and enables you to define the variable parameters. If you type a variable name that exists the Variable pop-up menu displays letting you select the variable from the list.
If you manually enter an existing variable name, make sure you enclose it in double brace brackets: {{variableName}}
Add variable panel
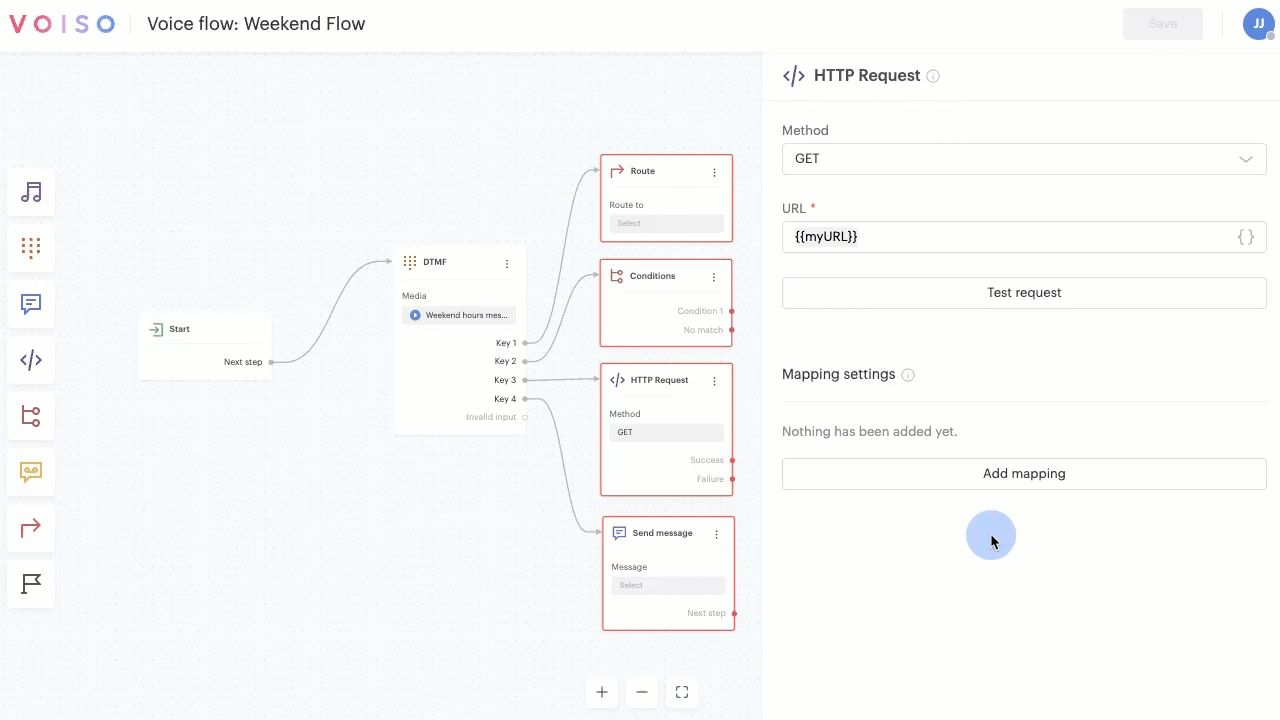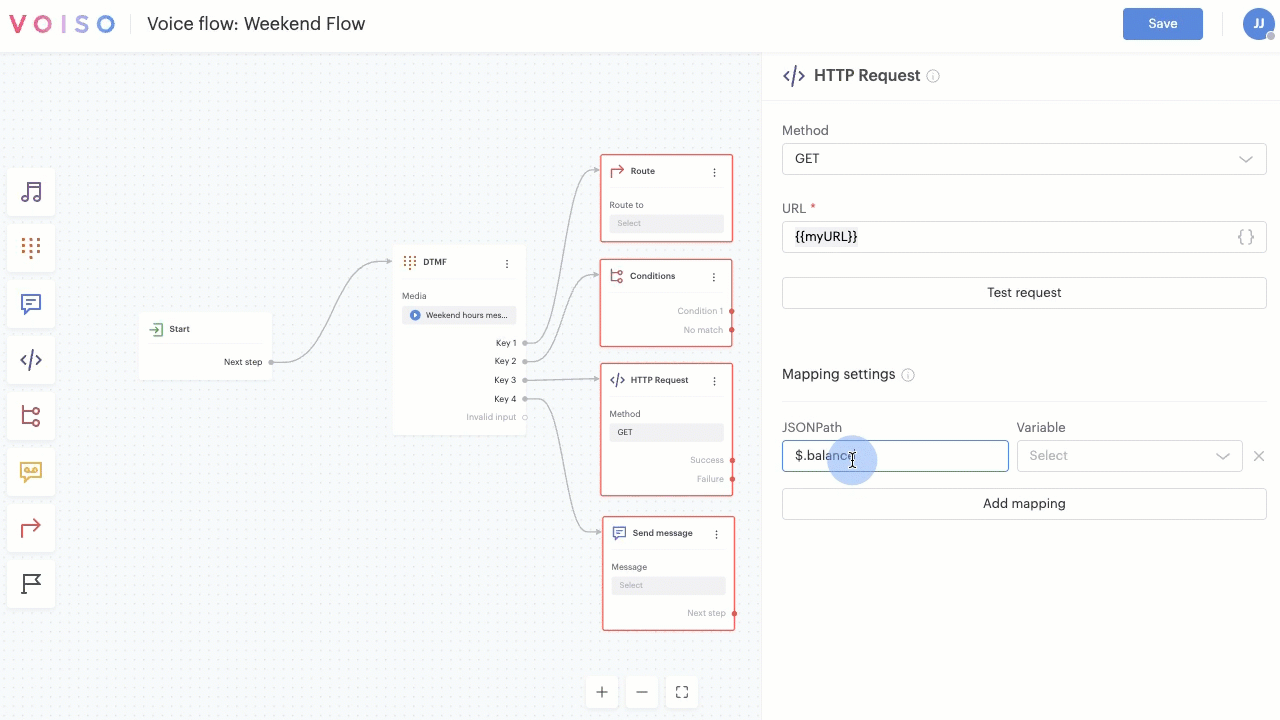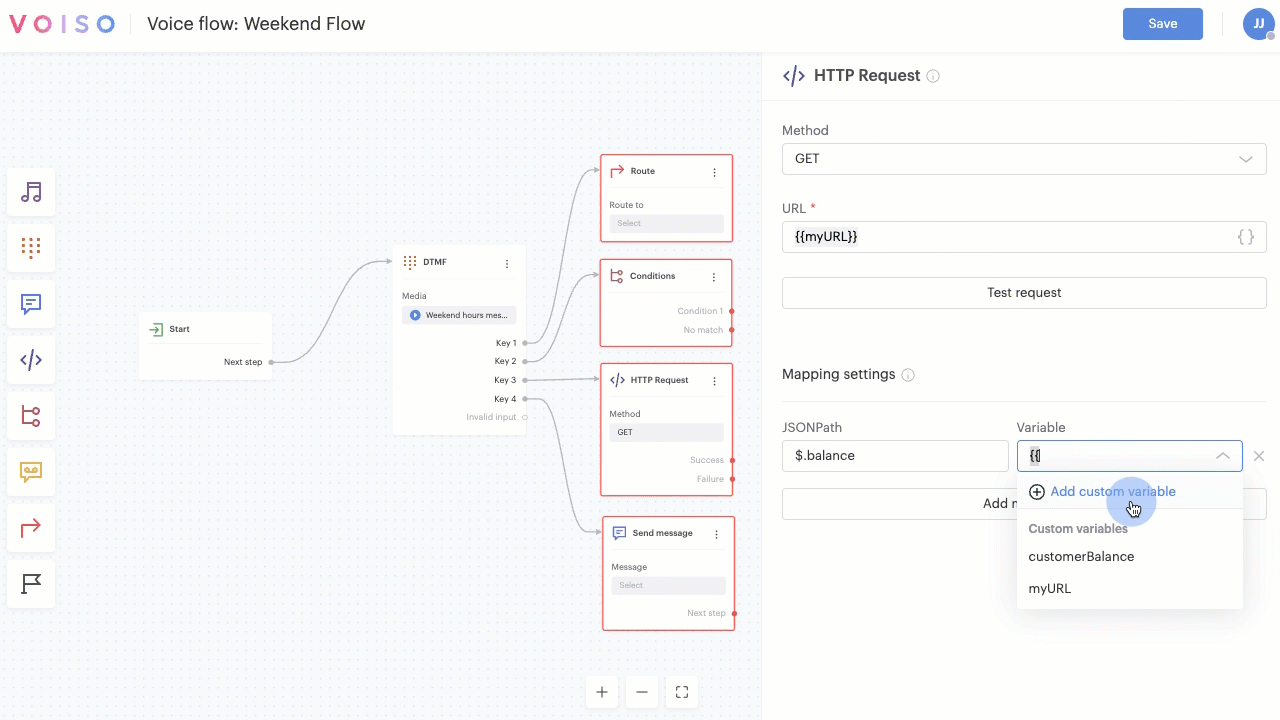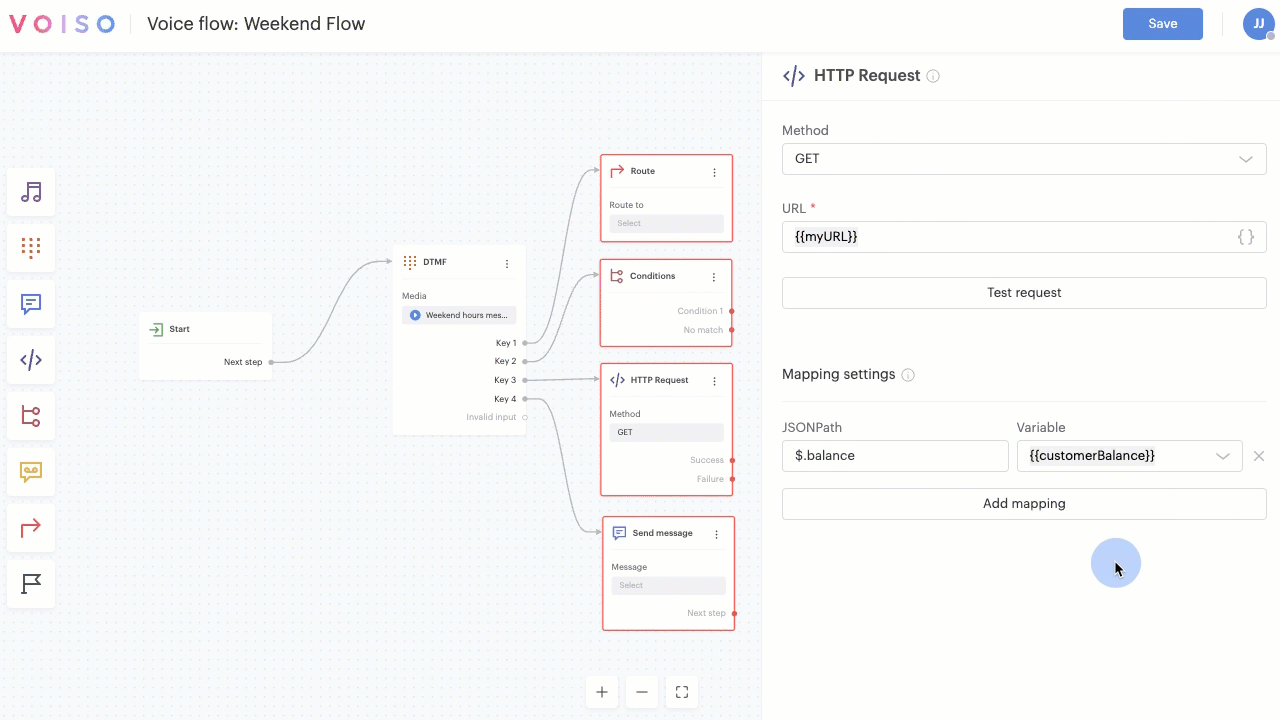
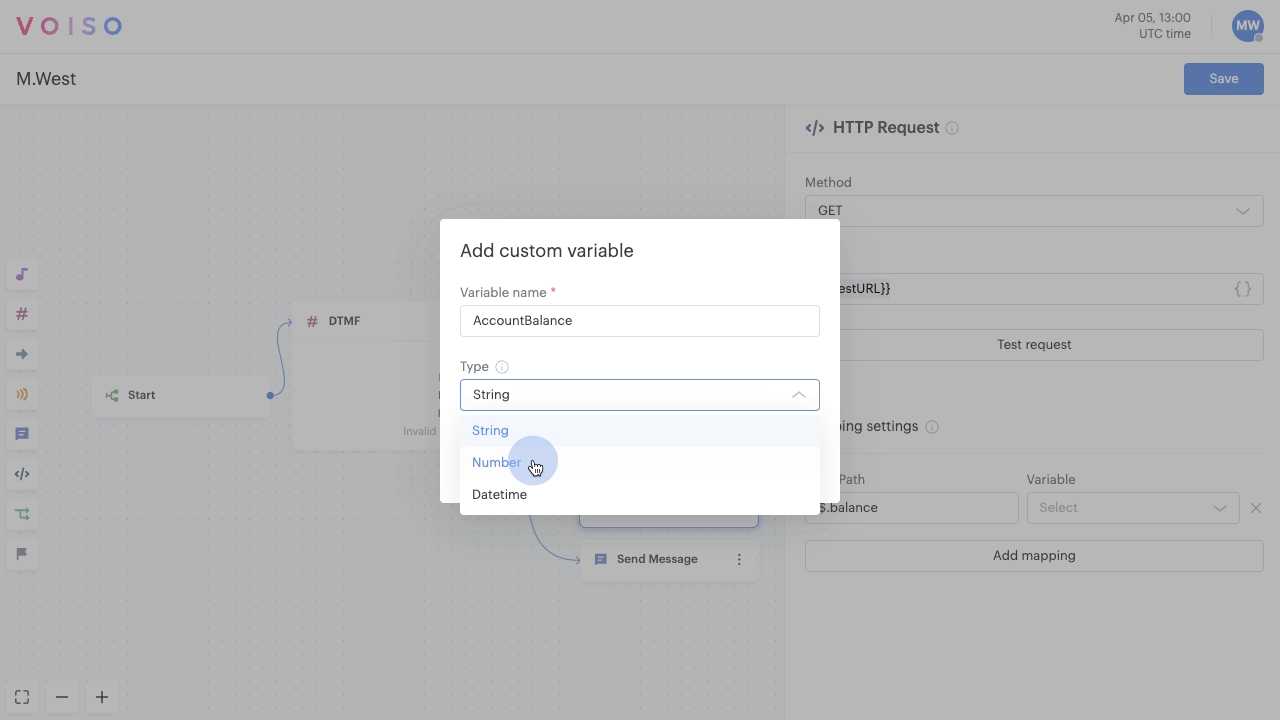
When custom variables are available for a node, Voiso enables you to either select an existing system or custom variable, or to create a new variable on-the-fly.
To create a new variable on-the-fly, select Add custom variable from the Variable menu.
In the Add custom variable panel, enter a unique name in the Variable name field. The name must be unique in the flow as variables are reusable across multiple nodes.
Use cases
The following sections include some suggestions for how you can leverage variables in your interaction flows.
Priority routing
You can leverage system and custom variables to implement priority routing. Create variables that relate back to contact and call information in your CRM. Use the ANI from the call to identify the contact. Use the HTTP request node to retrieve contact information from your CRM or the Voiso CDR API, including the extension of the last agent to handle an interaction with the contact. Use the retrieved extension to route the call to the agent if they are available.
Priority routing enables you to bypass the IVR and connect priority callers to specific agents or queues.
Dynamic content in SMS
Custom and system variables can be used with the Send message node to customize the content of SMS messages. For example, if a contact requests a payment link, you can use the ANI system variable to identify the caller in your CRM, use the HTTP request node to query your payment system API for the link and then automatically populate an SMS message with the link using a custom variable.
SMS dynamic content, powered by variables, offers a robust solution for populating SMS messages in response to customer inquiries. By integrating variables into the Send message node, you can tailor each message with personalized information based on the specific request. For example, when a customer seeks information about their account balance, variables can fetch real-time data from your data service and dynamically insert the relevant balance details into the SMS.
Dynamic content also enables you to personalize messages by inserting the contact's name and other personal information into the message.
Leverage significant personal dates
Variables can help you add a personal touch to your interactions. For example, you can identify significant dates for the contact, such as birthdays, culturally relevant holidays, anniversaries and milestones related to your business such as how long they have been a loyal customer, to encourage continued engagement.
When a contact calls on or near a significant date, you can automatically detect the date using the start_time system variable then compare it to significant dates in your CRM and automatically make special offers to the caller. Use the HTTP request node to obtain information from your data service and store it in a custom variable, then use the Conditions node to compare the timestamp with the relevant dates.
Saving contact responses
The Message node enables you to send a digital channels message to a contact and what for a response. The response can be saved in a variable and then used for conditional routing using the Conditions node or used to look up information from a data service using the HTTP request node.